Recovery from social anxiety and related conditions.
Subscriber numbers generate contributions that support scholarships for workshops.

“Dr. Mullen is doing impressive work helping the world. He is the pioneer of proactive neuroplasticity utilizing DRNI – deliberate, repetitive, neural information.” – WeVoice (Madrid, Málaga)
This is a general overview of Dr. Mullen’s Academa.edu course “Neuroscience and Happiness. Neuroplasticity and Positive Behavioral Change.”
Neuroplasticity is the scientific evidence of our brain’s constant adaptation to information. Scientists refer to the process as structural remodeling of the brain. It’s what makes learning and registering new experiences possible. All information notifies our neural pathways to restructure, generating a correlated change in behavior and perspective.
What is significant is our ability to dramatically accelerate learning by deliberately compelling our brain to repattern its neural circuitry. DRNI or deliberate, repetitive neural information empowers us to proactively transform our thoughts, behaviors, and perspectives, creating healthy new mindsets, skills, and abilities.
Thanks to advances in technology, researchers can get a never-before-possible look at the brain’s dynamic and malleable inner mechanics.
Three forms of neuroplasticity.
Reactive neuroplasticity is our brain’s natural and indeliberate adaptation to information. We react unconsciously to sensory information and insensible experiences: music, colors, sounds, tactile impressions, and phenomena. Whether it negatively or positively processes that information depends upon the content. Examples of positive reactions might be a warm bath, delightful company, or a child’s laughter. An adverse reaction might be rush-hour traffic, disappointment, or a hostile gesture.
Active neuroplasticity is achieved through intentional cognitive pursuits such as learning, engaging in social interaction, teaching, creating, or listening to music—not just hearing it but actively listening to it.
DRNI (deliberate, repetitive neural information) is proactive neuroplasticity—the deliberate repatterning of our neural network utilizing tools and techniques developed for the process. Proactive neuroplasticity through DRNI is the most potent and effective means of learning.
(1) it alleviates symptoms of ‘mental’ disorders and general discomforts that impact our emotional well-being and quality of life. A regimen of DRNI can compensate for and overwhelm decades of irrational and harmful thoughts and behaviors.
(2) The calculated regimen of repetitive neural input accelerates and consolidates learning. It facilitates the pursuit of our personal goals and objectives—eliminating a bad habit, self-transformation—harnessing our intrinsic aptitude for extraordinary living.
Space is Limited
Register Early
“It is one of the best investments I have made in myself, and I will
continue to improve and benefit from it for the rest of my life.” – Nick P.
* * *
Recovery from emotional dysfunction and the pursuit of goals and objectives are facilitated through the same process of DRNI.
Our brain is in constant flux; it never stops realigning to new information. Connections strengthen and weaken, neurons atrophy and others are born, learning replaces unlearning, chemical and electrical energy dissipates and expands, and functions shift from one region to another. Proactively stimulating our brain with deliberate, repetitive neural information accelerates and consolidates the process; there is a correlated change in thought, behavior, and perspective, becoming habitual and spontaneous over time.
Each neural input of information causes a receptor neuron to fire, transmitting chemical and electrical energy, from neuron to neuron throughout the nervous system. DRNI expedites the process. Multiple positive DRNI, such as a series of positive personal affirmations (PPAs), cause multiple receptor neurons to fire, dramatically amplifying learning through synaptic neurotransmission.
Hormonal and chemical neurotransmitters
Our brain rewards us with chemical and hormonal neurotransmissions: GABA for relaxation, serotonin and dopamine for pleasure and motivation, and endorphins for euphoria. In addition, it supplies us with chemicals and hormones that facilitate learning, memory, and concentration.
Life can be difficult; many of us are unsatisfied, unhappy, and nonproductive. When that information filters into our neural system, our neurotransmitters support that negativity. That’s why it’s so hard to break a bad habit and recovery is difficult. Conversely, every time we provide positive input, our brain releases those same chemicals and hormones, generating feelings of self-worth and healthy productivity. It generates the motivation, persistence, and perseverance to achieve our potential.
Our brain is an organic reciprocator.
Our human brain does not think; it is an organic reciprocator that allows us to think. Its job is to provide the chemical and electrical maintenance that supports our vital functions: heartbeat, nervous system, and blood–flow. Neural messages tell us when to breathe, stimulate thirst, and control our weight and digestion. Our brain does not differentiate rational from irrational thinking, healthy from toxic behaviors. Instead, it reacts to the positive or negative energy of the information.
Universal abundance
Our brain codes the health or toxicity of information into negative or positive electrical energy. That energy, duplicated by millions of participating neurons, is reciprocated in abundance because a single neuron receptor ultimately engages millions of participating neurons, each with its energy transmissions. Our human brain contains 86 billion nerve cells or neurons arranged in pathways or networks based on that electrical activity. The reciprocating energy from DRNI is vastly more abundant because of the repeated firing of the neuron receptor. Positive energy in, positive energy multiplied millions of times, positive energy reciprocated in abundance.
Trajectory of Information
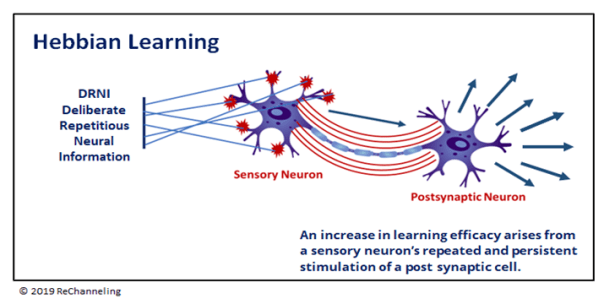
Neurons are the core components of our brain and our central nervous system. Inside each neuron is electrical activity. Information stimulates or excites a receptor neuron which fires, stimulating a presynaptic or sensory neuron via an axon or connecting pathway. Sensory neurons transmit the information to the synapse at the junction of the postsynaptic cell or relay neuron. The synapse permits the neurons to interact. The neuron’s hairlike tendrils (dendrites) pick up the synaptic signal and forward that information to the soma or nucleus of the cell body. Continuous electrical and chemical energy impulses engage millions of participating neurons, which transmit the electrical energy to millions of other neurons in multiple interconnected areas of our brain. Finally, the electrical energy converts back into information relayed by the motor neuron to its appropriate destination–our ears, bladder, muscles, and so on. Cognitive information is compartmentalized into the areas of the brain associated with the distinctly human traits of higher thought, language, and human consciousness.
Every input of information, intentional or otherwise, causes a receptor neuron to fire. Each time a neuron fires, it strengthens the axon connection and the neural bond. DRNI expedites the process through deliberate repetition. An increase in learning efficacy arises from the sensory neuron’s repeated and persistent stimulation of the postsynaptic cell. Multiple firings dramatically accelerate and consolidate learning. In addition, DRNI activates long-term potentiation, which increases the strength of the nerve impulses along the connecting pathways, generating more energy. BDNF or brain-derived neurotrophic factors are proteins that neurons need for survival. Deliberate, repetitive neural information generates higher levels of BDNF, which is associated with improved cognitive functioning, mental health, and memory.

Onset
Combined statistics evidence roughly 90% of neuroses onset at adolescence or earlier. In the event conditions like PTSD or clinical narcissism begin later in life, susceptibility originates in childhood as a consequence of childhood physical, emotional, or sexual disturbance(s). Our self-esteem and image are modified by experience and help form the foundation of our personality. We are who we are because of our core beliefs and the accumulation of our experiences. Since its onset, emotional dysfunction has been feeding our brains irrational thoughts and behaviors. Irrational is anything detrimental to our emotional well-being and quality of life.
Simply put, it is not logical or reasonable to cause ourselves harm. These irrational thoughts and behaviors compel us to feed our brains harmful and self-destructive information. The purpose of DRNI is to replace those perceptions of undesirability and unworthiness generated by our childhood disturbance(s).
Personal goals and objectives
The alternative utilization of DRNI is in the pursuit of our goals and objectives—improving life satisfaction, transforming ourselves, and becoming the best that we can be. We all know how difficult it is to change, remove ourselves from hostile environments, and break harmful habits that interfere with optimum functioning. We’re physiologically hard-wired to resist anything that disrupts our equilibrium. Our inertia senses and repels changes, and our brain’s basal ganglia resist any modification in behavior patterns. DRNI empowers us to assume accountability for our emotional well-being, productivity, and quality of life, by proactively controlling information input.
Hebbian Learning
Hebbian learning describes how neurons learn by responding to information. Hebb’s rule of neuroplasticity states that neurons that fire together wire together. In other words, the more neurons communicate with one another, the stronger the connection. When multiple neurons wire together, they create more receptor and sensory neurons. Repeated firing strengthens and solidifies the pathways between neurons. Synaptic connections consolidate when two or more neurons are activated contiguously. The more repetitions, the quicker and more robust the new connection. The activity of the axon pathway is heightened, urging the synapses to increase and accelerate the release of chemicals and hormones. Conscious repetition of information correlates to more robust learning and unlearning.
We are physiologically acclimated to our condition. It has been developing within us since childhood. This is why it is challenging to establish new habits or change our self-image and outlook. Let us use the example of someone with social anxiety disorder. The predominant symptom of SAD is intense apprehension of social interaction—the fear of being judged, negatively evaluated and ridiculed. This causes persistent, pathological anxiety in everyday situations such as dating, interviewing for a position, or even answering a question in class.
Because our brain does not differentiate healthy from toxic information, each time a SAD person avoids a social situation or alienates someone out of fear of rejection, she or he is chemically and hormonally compensated. Self-destructive behaviors are rewarded with GABA for relaxation, dopamine for pleasure and motivation, endorphins for euphoria, and serotonin for a sense of well-being. We receive acetylcholine for our negativity, glutamate to support our selective memory, and noradrenaline to meddle with our concentration. Our brain says “Good job. Here is some more encouragement for your irrational behavior. “
Our neural network naturally adapts and restructures to information, whether reactive to unconscious experience or actively generated by our compulsion to engage and learn. Logic dictates that if our neural network learns from information, its deliberate, repetitive neural input enhances the process. If information naturally strengthens and consolidates neural connections to accelerate learning, then repetition dramatically expedites the process.
Positive Personal Affirmations
Positive personal affirmations are rational, reasonable, possible, goal-focused, and first-person or future time. Rational because the objective is subverting irrationality. Remember, it is illogical and unreasonable to cause ourselves harm. PPAs are fair and sensible reflections of our aspirations and intentions. The end goal must be possible, or the effort is counter-productive and futile. Goal-focused is self-explanatory; our path will be purposeless meandering if we do not know our destination. PPAs should be unconditional and to the point.
DRNI
The information at the core of DRNI is calculated and specific to our intention. Are we challenging the negative thoughts and behaviors of our dysfunction? Are we reaffirming the character strengths that generate the motivation and perseverance to accomplish? What is our end goal? What is the personal milestone we desire to achieve? The crucial element of DRNI is the content of the intention behind the information. The strength of the message correlates to its durability and learning efficacy.
So, what is the content of deliberate, repetitive neural information, how is it constructed, and what materials are helpful to its construction? CBT, positive psychology, and other positive approaches collaboratively work to develop the specific, intention-driven content of the positive personal affirmations at the core of DRNI.
Cognitive Self-Behavioral Modification
As light is the absence of darkness, so positive is the absence of negativity. Cognitive-behavioral therapy’s overarching objective is to replace irrational and unhealthy thoughts and behaviors with productive and emotionally affirming ones.
As our understanding of behavioral neuroplasticity evolved, it became clear that the practice of cognitive-behavioral modification produces changes in human brain activity. Further studies revealed that an effective way to counter the negativity generated by our dysfunction or discomfort is through the cognitive aspect of CBSM, the deliberate, repetitious input of positive information. Over time and through repetition, new thoughts and behaviors become habitual and spontaneous. Studies of CBM have shown it to be an effective treatment for various mental illnesses, including depression, social anxiety, generalized anxiety, panic, bipolar and eating disorders, PTSD, OCD, and schizophrenia. CBSM’s mechanisms of change are formidable tools in behavioral modification when utilizing repetitive cognitive reinforcement in concert with other approaches. The behavioral aspect supports the process Positive personal affirmations, embraced by us for centuries, are the cognitive aspect of CBSM.
Positive Psychology
Positive psychology is the most viable adjunct to cognitive-behavioral modification in the processing of DRNI. Although the program functions best in conjunction with other approaches, its focus on the positive aspects of human development and achievement not only improves our self-image and perspectives but greatly enhances overall psychological and physiological health.
Positive psychology describes the pursuit of recovery and goals and objectives as people determining their potential and purpose by constructing and reclaiming a valued and welcoming identity. Its emphasis is on recognizing and regenerating our inherent character strengths, virtues, and attributes, which underscore our creativity, optimism, resilience, empathy, compassion, humor, and life satisfaction. It facilitates this through mindfulness, autobiography, positive writing, gratitude, forgiveness, kindness, and other self-affirming techniques. The overarching objective of positive psychology is to identify our inherent assets and capabilities to achieve our potential to become the best that we can be.
Accepting scientific validity to approaches that support DRNI encourages us to control our dysfunction or discomfort and achieve our motivating personal concerns. Achieving recovery and motivating personal concerns are not overnight achievables, however. The process is simple in theory but challenging due to the commitment and endurance required for the long-term, repetitive process of proactive neuroplasticity. We do not put on tennis shorts and advance to Wimbledon without decades of practice with racket and balls; philharmonics cater to pianists who have spent some time at the keyboard. DRNI requires a calculated regimen of deliberate, repetitive neural information. We can have all the tools we require, but they need to come out of the shed. Not only is DRNI repetitious and tedious, but it also fails to deliver immediate tangible results, causing us to readily concede defeat and abandon hope in this era of instant gratification.
Recommended Practice: Repeat three positive personal affirmations a minimum of 5 times daily. That is about five minutes of your time.
Proactive Neuroplasticity YouTube Series
* * *
WHY IS YOUR SUPPORT SO IMPORTANT? ReChanneling develops and implements programs to (1) mitigate symptoms of social anxiety and related conditions and (2) pursue personal goals and objectives – harnessing our intrinsic aptitude for extraordinary living. Our paradigmatic approach targets the personality through empathy, collaboration, and program integration utilizing neuroscience and psychology including proactive neuroplasticity, cognitive-behavioral modification, positive psychology, and techniques designed to regenerate self-esteem. All donations support scholarships for groups and workshops.
Dr. Mullen is doing impressive work helping the world. He is the
pioneer of proactive neuroplasticity utilizing DRNI—deliberate,
repetitive, neural information. WeVoice.



